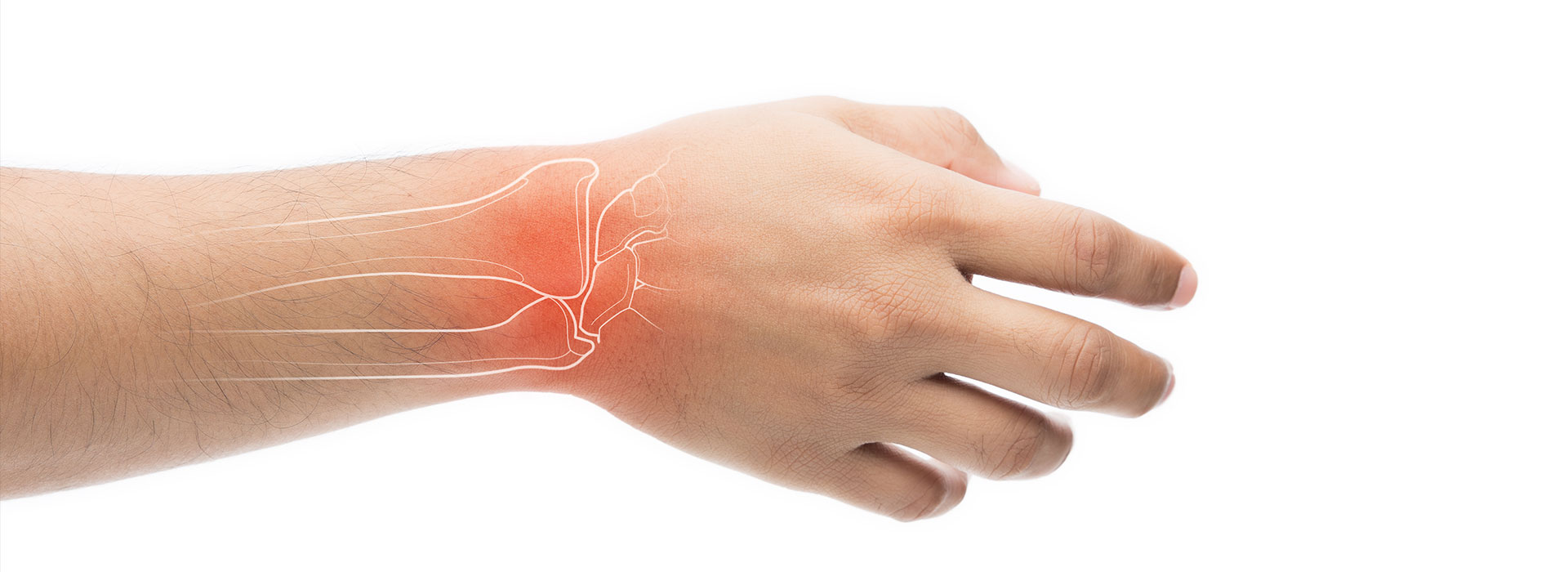
Carpal tunnel syndrome STC, also called carpal tunnel syndrome, represents the damage to the median nerve through its compression at the level of the wrist. The carpal tunnel is an anatomical formation located at the base of the hand (wrist) that constitutes a narrow passage, delimited by the carpal bones and the retinaculum of the flexors (transverse carpal ligament) and is crossed by the median nerve and nine tendons.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs mainly in women, aged between 30 and 50 years. When CTS is not diagnosed and treated, it can get worse over time. In the early stages, carpal tunnel syndrome is manifested by pain and numbness of the area, sometimes with a burning and tingling sensation.
Carpal tunnel syndrome – causes
What are the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome – causes
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a compression neuropathy that is due to the inflammation of the tendons contained by the carpal tunnel or of the fist joint that causes the narrowing of the carpal tunnel.
The conditions that can favor the occurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome through compression of the median nerve at the level of the first joint are:
- Tumor formations such as lipomas or neurofibromas of the hand
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Amyloidosis
- Rheumatoid polyarthritis.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy favor the accumulation of fluid at the interstitial level, which can cause the transient appearance of carpal tunnel syndrome with spontaneous remission after birth
Professional factors that involve repetitive hand movements (tennis players, climbers) or maintaining a vicious position for a long time (hand on the mouse) are frequently involved in the occurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
What are the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
In the initial stages of the condition, carpal tunnel syndrome is manifested by the feeling of numbness and tingling in the I-IV fingers that appear more frequently during the night.
The evolution of the disease causes the appearance of annoying nocturnal pains that wake the patient from sleep, which can be accompanied by tremors and muscle weakness of the affected hand, lack of coordination of movements and atrophy of the flexor and extensor muscles of the fingers. In severe cases, carpal tunnel syndrome can progress to the appearance of ischemia of the median nerve with its necrosis and loss of sensitivity and functionality in the case of fingers I-IV.
Carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is established based on:
- Anamnesis
- Specialized clinical consultation
- Paraclinical investigations such as electromyography to determine the degree of damage to the median nerve and ultrasound of soft parts to highlight structural changes at the level of the carpal tunnel. X-rays of the hand and the fist joint are used to rule out fractures and degenerative joint diseases such as arthrosis
- Paraclinical laboratory investigations are performed to establish the etiology of carpal tunnel syndrome and include determinations of the glycemic index, thyroid hormones, rheumatoid factor or renal function parameters (urea, creatinine, glomerular filtration rate)
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
Symptomatic treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome involves:
- Administration of oral anti-inflammatory drugs
- Local infiltrations at the level of the carpal tunnel
- Physiotherapy
- Wearing medical orthoses to immobilize the affected wrist
The etiological treatment involves a surgical intervention to decompress the nerve by sectioning the fibrous structure of the transverse carpal ligament, by the classic open method or by endoscopic approach.
References:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome –https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMcp013018
- The Carpal-tunnel Syndrome: Clinical Evaluation of 598 Hands – https://journals.lww.com/corr/citation/1972/03000/the_carpal_tunnel_syndrome__clinical_evaluation_of.7.aspx
- The carpal tunnel syndrome. A study of carpal canal pressures – https://europepmc.org/article/med/7204435


You helped me a lot by posting this article and I love what I’m learning.