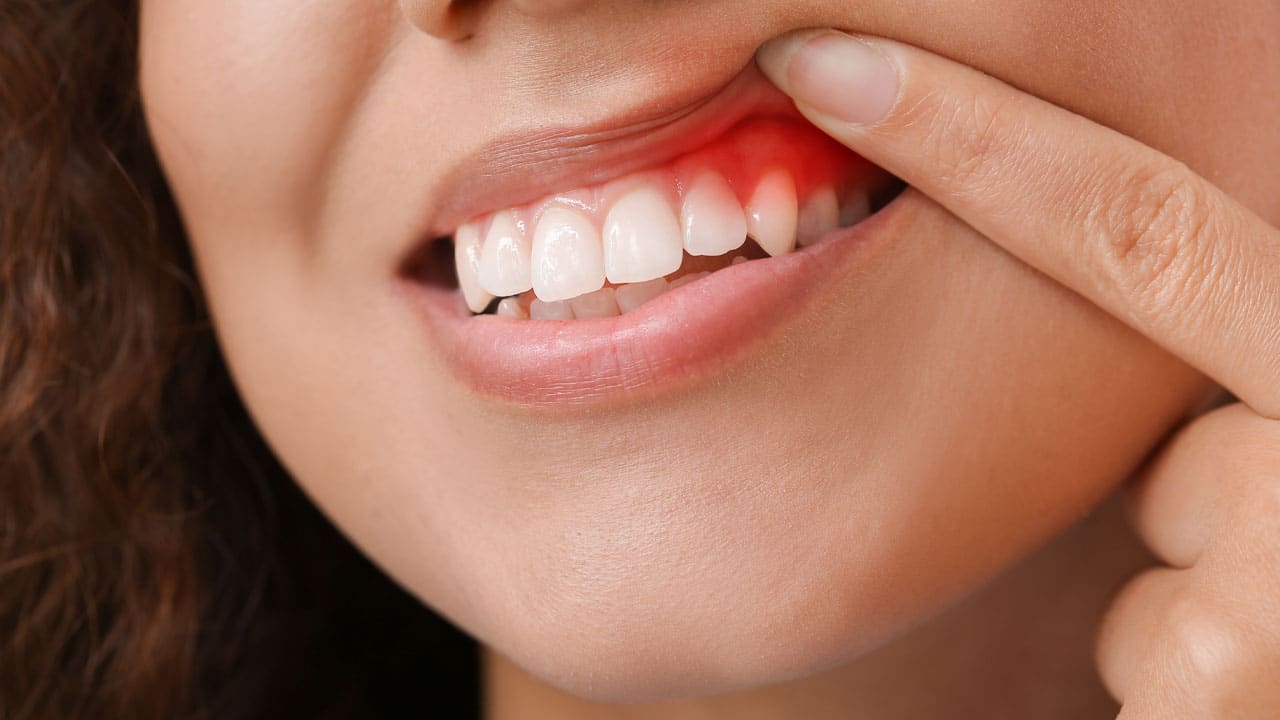
Gingivitis is a superficial inflammation of the gums and is the first stage of periodontal disease. Gingivitis is a reversible condition that if treated early can prevent the loss of teeth and other secondary complications (periodontal disease).
What are the symptoms of the condition
Treatment methods of the disease
What is gingivitis
Gingivitis is a superficial inflammation of the gums and is the first stage of periodontal disease. Gingivitis is a reversible condition that if treated early can prevent the loss of teeth and other secondary complications (periodontal disease).
Why gingivitis occurs
Inflammation of the gums is favored by poor oral hygiene, which causes bacteria resulting from the breakdown of sugars in food scraps to accumulate in the oral cavity. The accumulation of dental plaque leads to an increase in the number of bacteria and, over time, its solidification causes the appearance of dental tartar.
The risk factors that promote gum inflammation are:
- Smoking
- Older age
- Low dietary intake of vitamin C
- Dental implants, and orthodontic appliances that hinder plaque removal by brushing
- Heredity
- Hormonal fluctuations that alter the body’s immune response to plaque aggression
- Immune system deficiencies
What are the symptoms of the condition
The symptoms of gingivitis are represented by the redness and irritation of the gums, which can bleed easily during tooth brushing, thus favoring the penetration of bacterial agents through the continuity solutions created on the surface of the gingival soft tissues. The chronic evolution of the condition can lead to dental caries, periodontal disease or even tooth loss.
Acute necrotizing gingivitis is rare and is manifested by pain, bleeding and ulceration of the oral cavity which can easily become infected.
The main symptoms of gingivitis are:
- Gingival inflammation
- Gingival hyperemia
- Gingival bleeding
- Bad breath
- Gingival retraction
Diagnosis of gingivitis
The diagnosis of gingivitis is established by the stomatologist after examination of the oral cavity and may require in certain situations dental X-rays to assess the health of the dental roots.
Treatment methods of the disease
The treatment methods used for gingivitis are professional brushing and ultrasonic scaling carried out in dental surgeries, which can be complemented by restorative procedures and adjustment of older dentures that hinder proper hygiene of the oral cavity.
The health of the gums can be maintained by removing bacterial plaque during oral hygiene including flossing and mouth washing twice a day, adopting a balanced diet and dental check-ups are very important to be carried out periodically every 6 months or 1 year.
Find out more:
- Gingivitis – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1600-051X.1986.tb01471.x
- Experimental Gingivitis in Man – https://aap.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1902/jop.1965.36.3.177
- Epidemiology of gingivitis – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1600-051X.1986.tb01473.x