What are the causes of strabismus?
What are the diagnostic methods of strabismus
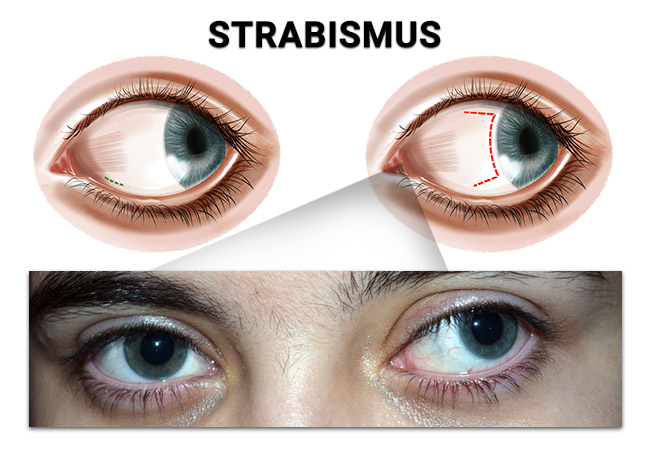
What is strabismus?
Strabismus is a condition in which the alignment of the eyeballs is not parallel. The condition can manifest in one eyeball or more frequently in both eyes and can be present at birth in a congenital form or can appear later in life – acquired strabismus.
What are the causes of strabismus?
The favoring factors of strabismus are represented by:
- Heredity – especially the heredity of refractive errors (myopia, hypermetropia – more commonly associated with convergent strabismus, astigmatism)
- Diseases of the central nervous system
- Neonatal neurological antecedents – prematurity, meningitis, hydrocephalus
- Cranial or orbital trauma
- The difference in diopters between the two eyes
- Brain tumors
- Chromosomal defects – Down syndrome
How the condition manifests itself
The coordination of the position and movements of the eyeballs is carried out by the central nervous system and carried out with the help of 6 muscles for each eye separately: 2 horizontal, 2 vertical and 2 oblique. Depending on the damage to a certain muscle, a specific deviation of the eye appears, strabismus can be of 3 types:
- convergent deviation (the eye runs towards the nose)
- divergent strabismus (the eye moves towards the temple)
- vertical strabismus (the eye runs up or down)
Along with the incorrect alignment of the eyeballs, patients with strabismus associate diplopia (double vision), defective depth perception, frequent blinking and tilting of the head to improve vision.
What are the diagnostic methods of strabismus
The diagnosis of squint deviation is established during an ophthalmological consultation performed by a specialist doctor. If there are people with this condition in the family, it is recommended to check with the ophthalmologist as early as possible in the case of children (before the age of 1 year).
Treatment of the disease
The goal of the treatment is to obtain optimal visual acuity in both eyes, reduce squint deviation and obtain or improve binocular vision.
The treatment of the congenital form must be carried out in the first 6 months of life to develop normal binocular vision and can be carried out through surgical correction or with the help of eyeglasses but also patches applied to the level of the healthy eye to force the child to use the affected eye. Eye drops for temporary blurring of vision and orthoptic exercises can be recommended to strengthen the eye muscles.
The surgical correction of strabismus is performed under general anesthesia with the aim of strengthening the muscles of the eyeballs, having a short postoperative recovery time. If the eyes do not realign completely, the surgical treatment can be repeated to obtain the expected results.
Adults benefit from the same treatment methods as in the case of children, and the chances of success increase in case of presentation to the ophthalmologist as early as possible.
Find out more:
- Epidemiology of strabismus. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1214733/
- Psychosocial Aspects of Strabismus Study – https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/640327
- Strabismus in Infancy – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0161642089329320